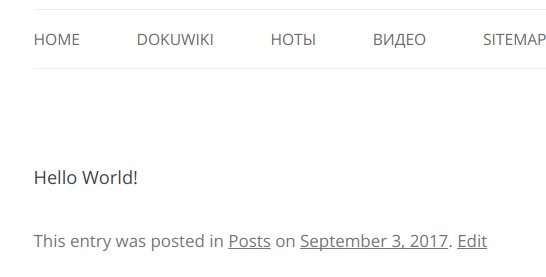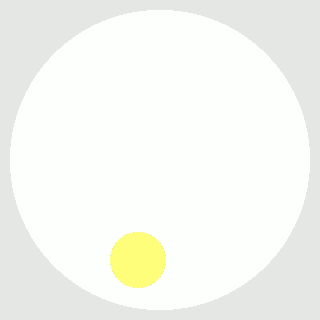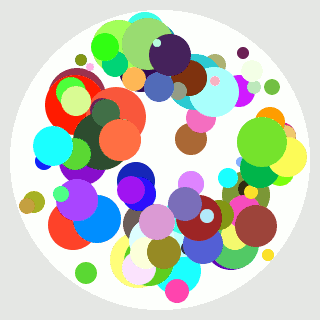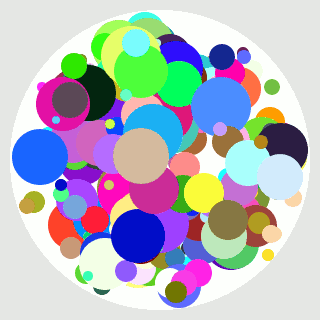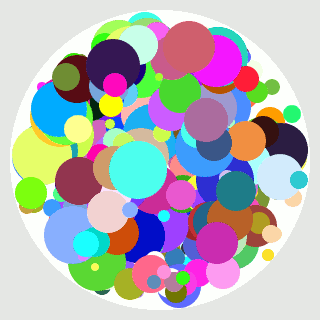
При помощи Кайро точку нарисовать просто, но как рассчитать, чтоб точка не вылазила за пределы круга?
– При помощи теоремы Пифагора.
Cairo – библиотека 2D векторной графики.
Python – интерпретатор и программный язык.
Мы рассмотрим только пример X координаты. Круг, как известно, квадратный, а Пифагоровы штаны во все стороны равны, поэтому для Y координаты все расчеты будут те же самые, только с другими буквами.
Нулевая точка XY координат в Cairo начинается в левом верхнем углу картинки. X0 – по горизонтали, Y0 – по вертикали. А координаты круга начинаются в середине картинки и отстоят от Cairo на расстояние радиус + каёмка в 10 пикселей.
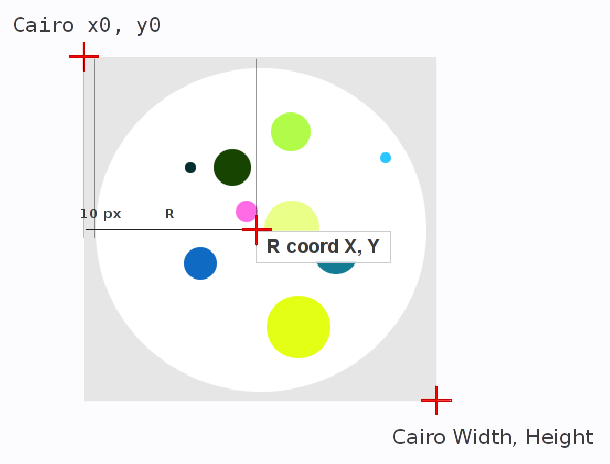
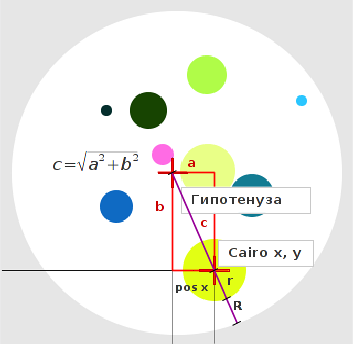
Поэтому относительно центральной точки (нулевой для круга) мы отнимаем абсолютные значения xy позиции точки, чтоб узнать относительную величину сторон квадрата, диагональ которого не должна превышать расстояние разницы радиуса круга и радиуса точки.
a=X-x
Если условие выполнимое, мы считаем координаты точки приемлемыми, а если нет, то игнорируем их.
Мы оперируем абсолютными значениями числа без учета его знака, потому что местоположение точки относительно центра круга нам безразлично.
abs(a)
Нас интересует длиннее ли диагональ прямоугольника длины R радиуса круга минус r радиуса точки или нет.
if math.sqrt(abs(a) ** 2 + abs(b) ** 2) < R-r
Если нет, то точка хорошая, и мы ее рисуем. Если да – точка плохая, мы ее пропускаем и при помощи генератора случайных чисел получаем следующую.
x = random.randint(0, WIDTH)
Код для Питона 2.7
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cairo, random, math
''' Random dot in circle. '''
R=150 # Радиус круга
r=10 # Радиус точки
n=300 # Количество PNG фрэймов для анимации
############################################
WIDTH, HEIGHT = R*2+20, R*2+20 # Длина и ширина картинки + каемка в
# 10 пикселей с каждой стороны.
X=WIDTH/2 # X позиция круга
Y=HEIGHT/2 # Y позиция круга
surface = cairo.ImageSurface (cairo.FORMAT_ARGB32, WIDTH, HEIGHT)
context = cairo.Context (surface)
# Серый задний план -----------------
context.set_source_rgb(0.9, 0.9, 0.9)
context.rectangle(0, 0, WIDTH, HEIGHT)
context.fill()
# Белый круг на заднем плане --------
context.set_source_rgb(1, 1, 1) # белый цвет круга в rgb формате
context.arc(X, Y, R, 0, 360)
context.fill()
i=0
while i < n+1:
x = random.randint(0, WIDTH) # абсолютные координаты точки на оси X
y = random.randint(0, HEIGHT) # абсолютные координаты точки на оси Y
a=x-X # относительное положение точки по отношению к центру круга
b=y-Y
r=random.randint(4, 30) # Случайный радиус точки от 4 до 30 пикселей
if math.sqrt(abs(a) ** 2 + abs(b) ** 2) < R-r:
# Случайная точка -------------------
r_=random.random()*1.2 # Цвет в rgb формате, случайные значения.
g_=random.random()*1.2
b_=random.random()*1.2
context.set_source_rgb(r_, g_, b_)
context.arc(x, y, r, 0*math.pi/180, 360*math.pi/180)
context.fill()
print i, 'x:',x,'y:',y
filename='frame_'+'0'*(len(str(n))-len(str(i)))+str(i)+'.png'
surface.write_to_png (filename) # Сохраняем фрэйм в PNG файл.
i+=1